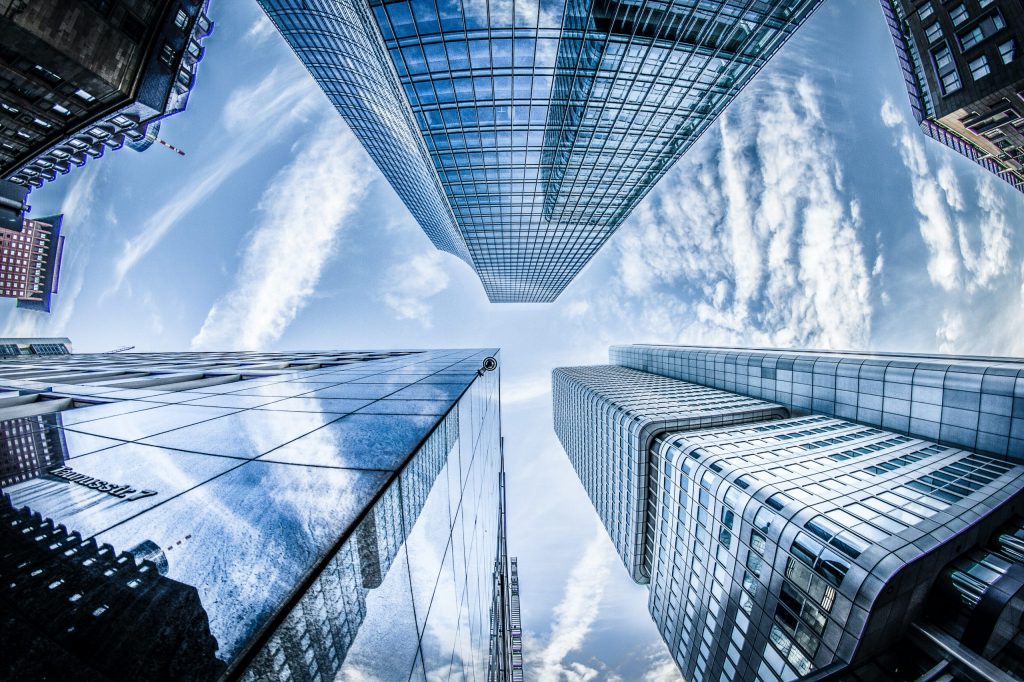
What is the cloud? “The cloud” is simply computer servers that are accessed over the Internet, along with the software and databases that run on those servers. Cloud servers are located in data centres worldwide. The Cloud, therefore, allows data to be stored ‘off-premises’.
Using cloud computing, users and companies don’t have to manage physical servers themselves or run software applications on their own machines. Data can be backed-up to the Cloud, providing for off-site backup and disaster recovery.
Access from anywhere (with an internet connection)
The cloud allows you to access the same files and applications from almost any device, because the computing and storage takes place on servers in a data centre, instead of locally on the user device. This is why you can log into your Instagram account on a new phone after your old phone breaks and still find their old account in place, with all your photos, videos, and conversation history. It works the same way with cloud email providers like Gmail or Microsoft Office 365, and with cloud storage providers like Dropbox or Google Drive.
For businesses, switching to cloud computing removes some costs and overhead: for instance, they no longer need their own servers. This especially makes an impact on small businesses that may not have been able to afford their own internal infrastructure but can outsource their infrastructure needs affordably. It can also make it easier for companies to operate internationally because employees and customers can access the same files and applications from any location.
How does the Cloud work?
Cloud computing is made possible by virtualization. Virtualization allows for the creation of a simulated, digital-only “virtual” computer that behaves in the same way as a physical computer, called a virtual machine. Virtual machines on the same host machine are ‘sandboxed’ from one another, so they don’t interact with each other at all, and the files and applications from one virtual machine aren’t visible to the other virtual machines even though they’re on the same physical machine.
Virtual machines also make more efficient use of the hardware hosting them. By running many virtual machines at once, one server becomes many servers, and a data centre becomes a whole host of data centres, able to serve many organizations. Thus, cloud providers can offer the use of their servers to far more customers at once than they would be able to otherwise, and they can do so at a low cost.
Even if individual servers go down, in general, you should always be online and always available. Cloud vendors generally back up their services on multiple machines and across multiple regions.
Contact Fresh Mango to find out how best to make use of the Cloud for your business.
Users access services either through a browser or through an app, connecting over the Internet – that is, through many interconnected networks – regardless of what device they’re using.